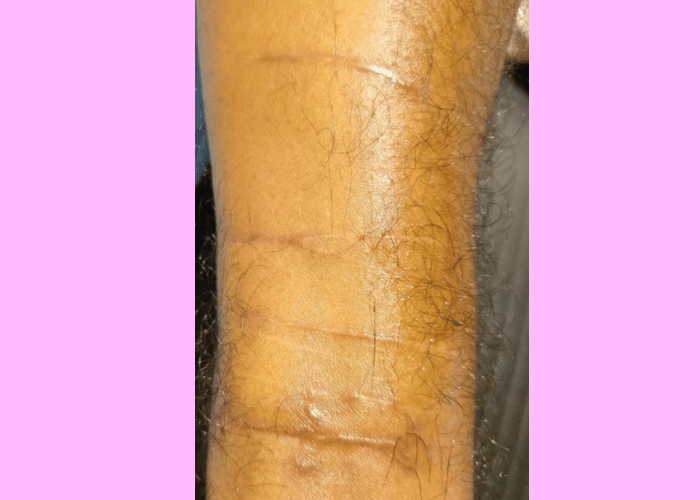
Self-harm scars are the physical marks left on the skin from intentional self-inflicted injuries. These scars can be a source of distress and may impact an individual’s self-esteem and mental health. Understanding how to manage and reduce the appearance of these scars can be an important step in the healing process.
Types of Self-Harm Scars
- Keloid Scars :
- Raised and thick scars that extend beyond the original wound area.
- Often darker in color than the surrounding skin.
- Hypertrophic Scars :
- Raised scars similar to keloids but confined to the original wound site.
- Can be red or pink and may fade over time.
- Atrophic Scars :
- Indented or sunken scars caused by the loss of underlying tissue.
- Often seen as pits or depressions on the skin.
- Contracture Scars :
- Scars that cause the skin to tighten, potentially restricting movement.
- Common with burns or extensive tissue damage.
Treatment and Management Options
1. Topical Treatments :
- Silicone Sheets and Gels : Helps flatten and soften scars over time.
- Vitamin E : Promotes healing and can improve the appearance of scars.
- Hydroquinone Creams : Lightens hyperpigmented scars.
2. Medical Treatments :
- Laser Therapy : Uses focused light to reduce redness, flatten raised scars, and improve skin texture.
- Microneedling : Creates micro-injuries to stimulate collagen production and improve scar appearance.
- Corticosteroid Injections : Reduces inflammation and flattens raised scars.
- Chemical Peels : Removes the top layer of skin to reduce the appearance of superficial scars.
- Dermal Fillers : Fills in indented scars to create a more even skin surface.
3. Surgical Treatments :
- Scar Revision Surgery : Removes or reduces the scar’s visibility by changing its appearance or location.
- Skin Grafting : In severe cases, healthy skin is transplanted to replace scarred areas.
4. Alternative Treatments :
- Massage Therapy : Regularly massaging the scar can help break down dense scar tissue.
- Onion Extract Gel : Has anti-inflammatory properties that may reduce scar size and redness.
Psychological and Emotional Support
1. Therapy and Counseling :
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) : Helps address the underlying causes of self-harm and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Support Groups : Provides a safe space to share experiences and receive support from others who understand.
2. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques :
The following practices can help manage stress and reduce the urge to self-harm.
- Meditation.
- Yoga.
- Deep breathing.
3. Creative Outlets :
- Engaging in art.
- Writing.
- Music.
- Dance.
All the above can provide an alternative way to express emotions.
Preventive Measures
- Identifying Triggers :
Understanding and avoiding situations or emotions that lead to self-harm.
- Healthy Coping Strategies :
Developing skills to manage
- Stress.
- Anxiety.
- Emotional pain without resorting to self-harm.
- Professional Help :
Seeking help from mental health professionals to address underlying issues such as
- Depression.
- Anxiety.
- Trauma.
Conclusion
Managing and reducing the appearance of self-harm scars involves a combination of medical treatments, emotional support, and preventive measures. Consulting a cosmetic surgeon can help determine the best course of action tailored to individual needs. Healing from self-harm is a multifaceted process that includes addressing both physical scars and the underlying emotional and psychological issues.
Have Any Question?
Feel free to call, e-mail or WhatsApp us with any questions you have about our services or to schedule an appointment.
- (+91) 9444437698
- info@silkee.beauty
- (+91) 7200037698
