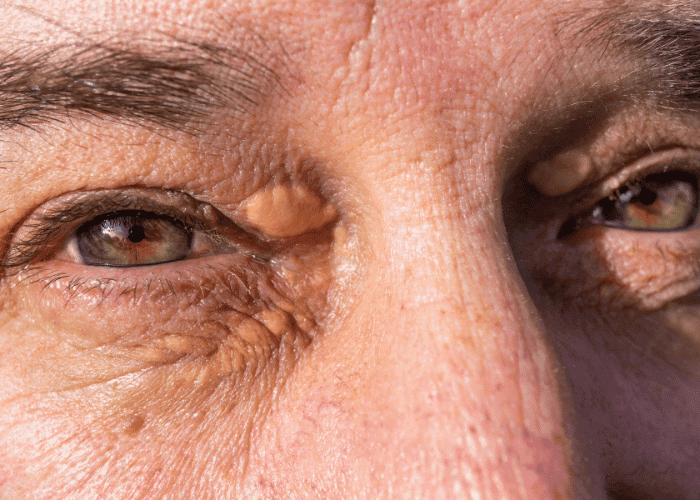
Xanthelasma are yellowish deposits of cholesterol that develop under the skin, typically around the eyelids. While they are not harmful or painful, they can be a cosmetic concern for many individuals.
Reason for xanthelasma
- Cholesterol Levels : High cholesterol levels, especially LDL cholesterol, can contribute to the development of xanthelasma.
- Genetic Factors : A family history of xanthelasma or high cholesterol can increase the risk.
- Medical Conditions : Conditions like diabetes, liver disease, and certain inherited lipid disorders can be associated with xanthelasma.
Clinically
Flat, papular, plaque and nodular variants. The last two variants are important because of the depth of infiltration, that makes them unresponsive to most methods except surgery.
Diagnosis
Physical Examination : A doctor can usually diagnose xanthelasma based on its appearance.
Blood Tests : To check cholesterol and lipid levels, as well as other underlying conditions.
Treatment
Lipid-Lowering Therapy : Medications to lower cholesterol levels may be prescribed if blood cholesterol is high.
Surgical Removal : Inspite of various techniques, recurrences are common. Recommend surgery for few, large lesions [plaques / nodular] with a appreciable depth.
Chemical Peels : Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels can sometimes be used with following specificatitons
- The concentration should be atleast 30- 70%.
- It is used in small lesion with little depth.
- Minimum 3-5 sessions are required for most lesions.
Electrodesiccation: A procedure that uses electric currents to remove the growths.
Laser therpy : Ablative lasers are superior to Ndyag, PDL, ruby, fractional lasers. Both Co2 and Erbium yag can be used.
Co2 laser : Because of coagulative effect ideal for deeper lesions.
Erbium yag lasers : Because of lack of coagulation, leads to a decrease in the achievable depth and may lead to recurrences.
Prevention measures
Diet and Exercise : Adopting a healthy diet low in saturated fats and regular exercise to maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
Medications : Taking cholesterol-lowering medications as prescribed.
Regular Check-Ups : Monitoring cholesterol levels and managing any underlying health conditions.
Prognosis
Recurrence : Xanthelasma can recur even after treatment, especially if cholesterol levels remain high.
Complications : Generally, xanthelasma do not lead to serious health issues, but they may indicate underlying health problems that need attention.
If you suspect you have xanthelasma, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate your cholesterol levels and discuss potential treatments.
Have Any Question?
Feel free to call, e-mail or WhatsApp us with any questions you have about our services or to schedule an appointment.
- (+91) 9444437698
- info@silkee.beauty
- (+91) 7200037698
